Chinese Labour Law Theory And Practice Understanding China: A Comprehensive Guide

Navigating the complexities of Chinese labour law is essential for businesses operating in or considering expanding into China. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of the theories, practices, and legal intricacies that govern employment relations in China, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate this dynamic legal landscape.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 791 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 516 pages |
Theoretical Foundations of Chinese Labour Law
Chinese labour law is rooted in a unique blend of socialist principles, Marxist theories, and Chinese cultural values. Understanding these theoretical foundations is crucial for interpreting and applying labour laws in practice:
- Socialist Principles: Labour is viewed as a fundamental right and a means of social progress. Employees are protected from exploitation and discrimination, and the state plays a role in promoting labour rights and welfare.
- Marxist Theories: Class struggle and the conflict between labour and capital shape the labour law framework. Workers are seen as having inherent rights and interests that must be protected.
- Chinese Cultural Values: Traditional Chinese values such as collectivism, harmony, and respect for authority influence the approach to labour relations and dispute resolution.
Key Labour Laws and Regulations
China has a comprehensive set of labour laws and regulations that govern various aspects of employment relations, including:
- Labour Contract Law: Establishes the legal framework for employment contracts, including terms and conditions, termination, and dispute resolution.
- Social Insurance Law: Provides for social insurance programs such as healthcare, pensions, and unemployment insurance.
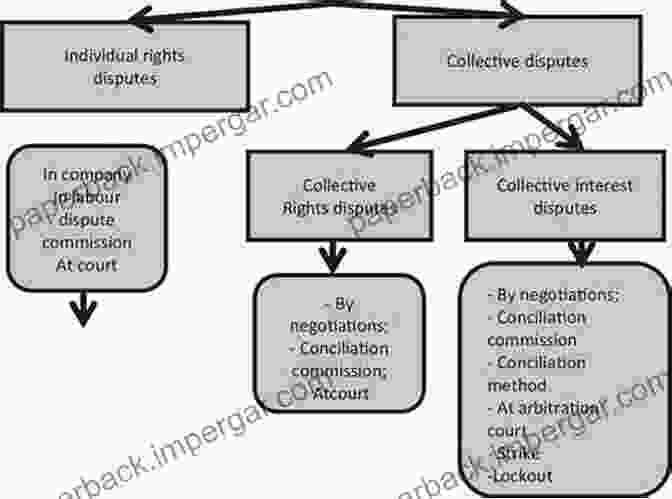
- Labour Dispute Mediation and Arbitration Law: Outlines the procedures for resolving labour disputes through mediation and arbitration.
- Trade Union Law: Recognizes the role of trade unions in representing workers' interests and promoting collective bargaining.
Labour Relations in Practice
The implementation of Chinese labour law in practice is influenced by a number of factors, including:
- Economic Development: Rapid economic growth has led to a shift towards a more market-oriented economy, impacting labour relations and employment practices.
- Globalization: China's integration into the global economy has brought new challenges and opportunities for labour law, such as the protection of migrant workers and the enforcement of international labour standards.
- Government Policies: Government policies play a significant role in shaping labour relations, including policies on minimum wage, social welfare, and labour market regulation.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its comprehensive legal framework, the implementation of Chinese labour law faces various challenges and controversies:
- Wage Arrears and Discrimination: Wage arrears and discrimination based on gender, age, and disability remain persistent issues in the Chinese labour market.
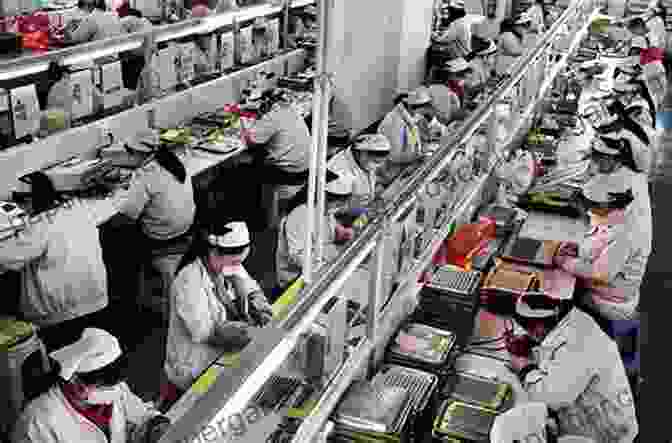
- Overwork and Safety Hazards: Long working hours and poor working conditions are common in certain industries, posing risks to workers' health and safety.
- Enforcement Difficulties: Limited enforcement resources and weak labour union representation can make it difficult to ensure compliance with labour laws.
Recent Developments and Future Trends
Chinese labour law is constantly evolving to address emerging challenges and trends:
- Amendments to Labour Laws: The Chinese government has been amending labour laws to enhance worker protection, promote labour flexibility, and adapt to changing economic conditions.
- Increased Labour Activism: Growing labour activism and the rise of independent labour unions have played a role in shaping labour law reforms.
- Technological Advancements: The impact of technology on the workplace is expected to continue to influence labour law, including issues related to automation, outsourcing, and the gig economy.
Understanding Chinese labour law theory and practice is essential for navigating the complexities of employment relations in China. By delving into the theoretical foundations, key laws, practical challenges, and recent developments, businesses and individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of this dynamic legal landscape. This knowledge empowers organizations to create harmonious and compliant workplaces, while safeguarding the rights and welfare of workers in China.
Image Alt Attributes
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 791 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 516 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Charles ReedUnlock Your Potential with the Power of Hypnosis: Discover Richard Nongard's...
Charles ReedUnlock Your Potential with the Power of Hypnosis: Discover Richard Nongard's... Galen PowellFollow ·4.3k
Galen PowellFollow ·4.3k Chase MorrisFollow ·10.8k
Chase MorrisFollow ·10.8k Ruben CoxFollow ·17.8k
Ruben CoxFollow ·17.8k Robert FrostFollow ·9.6k
Robert FrostFollow ·9.6k Federico García LorcaFollow ·9.8k
Federico García LorcaFollow ·9.8k Theo CoxFollow ·7.6k
Theo CoxFollow ·7.6k Stanley BellFollow ·2.7k
Stanley BellFollow ·2.7k Jamison CoxFollow ·19.4k
Jamison CoxFollow ·19.4k

 Jeffery Bell
Jeffery BellUnlock the Complexities of American Indian Law with...
Welcome to the...

 Louis Hayes
Louis HayesMaster Street Photography: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide
Are you ready to...

 Don Coleman
Don ColemanUnlock Your Business Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to...
Embark on a transformative journey with...

 Ruben Cox
Ruben CoxComparative Guide to International Competition Law: A...
` In today's interconnected global...

 Hamilton Bell
Hamilton BellElevate Your Bread-Making Skills: Unleash the Secrets of...
The Ultimate Guide for Novice Bakers to...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 791 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 516 pages |