Landmark Case Law: Exploring Historic US Supreme Court Rulings

The United States Supreme Court is the highest court in the land, and its decisions have a profound impact on American law and society. Over the years, the Court has issued a number of landmark rulings that have shaped the course of history. These rulings have defined individual rights, protected civil liberties, and established the balance of power within the American government.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 360 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 257 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
In this article, we will explore some of the most important landmark Supreme Court rulings. We will examine the facts of each case, the legal issues involved, and the impact that the ruling has had on American law and society.
Marbury v. Madison (1803)

Facts: In 1801, President John Adams appointed William Marbury to be a justice of the peace for the District of Columbia. However, Marbury's commission was not delivered before Adams left office. After Thomas Jefferson became president, he refused to deliver the commission. Marbury sued Madison, the new Secretary of State, to force him to deliver the commission.
Legal Issues: The case raised the question of whether the Supreme Court could Free Download the executive branch to do something. The Constitution gives the Supreme Court the power to interpret the law, but it does not explicitly give the Court the power to enforce its decisions.
Ruling: The Supreme Court ruled in favor of Madison. Chief Justice John Marshall wrote that the Court did not have the power to Free Download the executive branch to do something. However, Marshall also ruled that the Judiciary Act of 1789 was unconstitutional because it gave the Supreme Court the power to issue writs of mandamus, which are Free Downloads to government officials to do something.
Impact: Marbury v. Madison established the principle of judicial review. This means that the Supreme Court has the power to declare laws unconstitutional. This power is one of the most important checks and balances on the other branches of government.
McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)
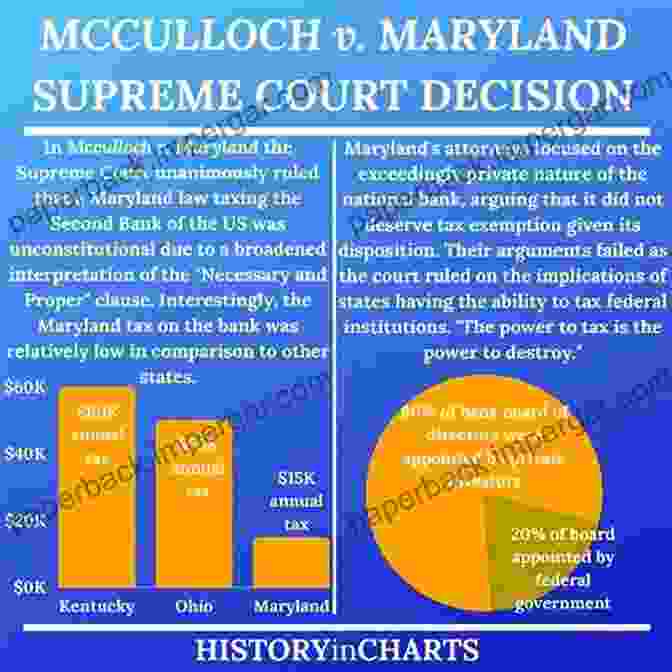
Facts: In 1816, Congress chartered the Second Bank of the United States. The bank established a branch in Maryland, and the state of Maryland imposed a tax on the bank. The bank refused to pay the tax, and the state sued.
Legal Issues: The case raised the question of whether Congress had the power to create a national bank. The Constitution does not explicitly give Congress the power to do so, but the bank's supporters argued that it was necessary for the government to function effectively.
Ruling: The Supreme Court ruled in favor of the bank. Chief Justice John Marshall wrote that Congress had the implied power to create a national bank because it was necessary to carry out its other powers, such as regulating commerce and raising revenue.
Impact: McCulloch v. Maryland established the principle of implied powers. This means that Congress has the power to do anything that is necessary to carry out its other powers. This principle has been used to justify a wide range of federal laws, from the creation of the Social Security system to the regulation of the Internet.
Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857)

Facts: Dred Scott was a slave who sued for his freedom in federal court. Scott argued that he was free because he had lived in a free state for several years. The Supreme Court ruled against Scott, holding that slaves were not citizens and therefore could not sue in federal court.
Legal Issues: The case raised the question of whether slaves were citizens of the United States. The Constitution does not explicitly define citizenship, but the Court held that slaves were not citizens because they were not considered to be persons under the law.
Impact: Dred Scott v. Sandford was a major turning point in the debate over slavery. The decision angered abolitionists and helped to push the country towards the Civil War.
Brown v. Board of Education (1954)

Facts: In 1951, a group of African American parents in Topeka, Kansas, sued the local school board, challenging the segregation of public schools. The Supreme Court ruled in favor of the parents, holding that segregation of public schools was unconstitutional.
Legal Issues: The case raised the question of whether the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment prohibited segregation of public schools. The Court held that it did, arguing that segregation created a sense of inferiority in African American children and denied them equal access to education.
Impact: Brown v. Board of Education was a major victory for the civil rights movement. The decision helped to end segregation of public schools and paved the way for other civil rights victories, such as the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
Roe v. Wade (1973)

Facts: In 1970, a young woman named Norma McCorvey sued the Dallas County District Attorney, Henry Wade, challenging the state's abortion law. The Supreme Court ruled in favor of McCorvey, holding that the Constitution protects a woman's right to have an abortion.
Legal Issues: The case raised the question of whether the Constitution protects a woman's right to have an abortion. The Court held that it does, arguing that the right to privacy includes the right to make decisions about one's own body.
Impact: Roe v. Wade is one of the most controversial Supreme Court rulings in history. The decision has been upheld by the Court several times, but it has also been the subject of numerous legal challenges. The debate over abortion continues to be a major issue in American politics.
The Supreme Court has issued a number of landmark rulings that have shaped the course of American history. These rulings have defined individual rights, protected civil liberties, and established the balance of power within the American government. The Supreme Court continues to play a vital role in American society, and its rulings will continue to shape our nation's future.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 360 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 257 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Eddie PowellUnlocking the Power of the Child's Brain: How Parents Can Use Neuroscience to...
Eddie PowellUnlocking the Power of the Child's Brain: How Parents Can Use Neuroscience to... Samuel WardFollow ·17.1k
Samuel WardFollow ·17.1k Corey HayesFollow ·7.7k
Corey HayesFollow ·7.7k Drew BellFollow ·12.3k
Drew BellFollow ·12.3k Haruki MurakamiFollow ·6.7k
Haruki MurakamiFollow ·6.7k Edgar HayesFollow ·10.7k
Edgar HayesFollow ·10.7k Junichiro TanizakiFollow ·3.3k
Junichiro TanizakiFollow ·3.3k Benjamin StoneFollow ·7k
Benjamin StoneFollow ·7k Dennis HayesFollow ·13.3k
Dennis HayesFollow ·13.3k

 Jeffery Bell
Jeffery BellUnlock the Complexities of American Indian Law with...
Welcome to the...

 Louis Hayes
Louis HayesMaster Street Photography: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide
Are you ready to...

 Don Coleman
Don ColemanUnlock Your Business Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to...
Embark on a transformative journey with...

 Ruben Cox
Ruben CoxComparative Guide to International Competition Law: A...
` In today's interconnected global...

 Hamilton Bell
Hamilton BellElevate Your Bread-Making Skills: Unleash the Secrets of...
The Ultimate Guide for Novice Bakers to...
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 360 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 257 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |